Control the use of antibiotics
- Excessive consumption
- Unappropriate use
Bacterial resistance is a major public health issue
That led, since 1998, the World Health Organization (WHO) to drafting various reports on the "bacterial threat", in collaboration with the european Union and United States.
Globally, excessive consumption of antibiotics by humans and animals follows trends observed in the EU.
Thus, that of livestock would now reach 60 000 tons. In addition, the increase in intensive livestock production, as a consequence of the increase in meat consumption in emerging countries, predicts a use of more than 100 000 tons by 2030, if no action is rapidly implemented.
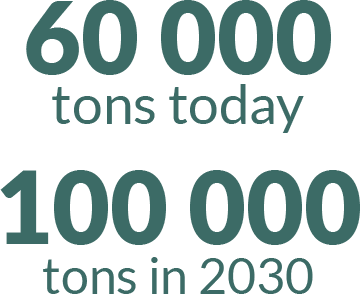
A phenomenon that has no geographical limit
The alarm signal pulled by the European community helped to raise international awareness.
The overall phenomenon of antibiotic resistance is thus clearly fuelled by the use of antibiotics in human and veterinary therapy.
The national action plan "Ecoantibio" has set the goal of reducing their consumption by 50% by 2020. It mobilizes all stakeholders in the livestock sectors, for responsible use of antibiotics.